It must be said that the suffering caused by psoriasis is underestimated by others. According to scientists, the negative impact of psoriasis on the quality of life is no worse than chronic heart failure and chronic lung diseases.
This disease does not kill directly, but it greatly destroys people's lives.
Let's talk about psoriasis.
It is a chronic inflammatory process of the skin, which modern medicine calls autoimmune, i. e. it is related to an allergy to his own tissues.
Psoriasis is one of the most common skin diseases and occurs in 1-2% of the population in developed countries.
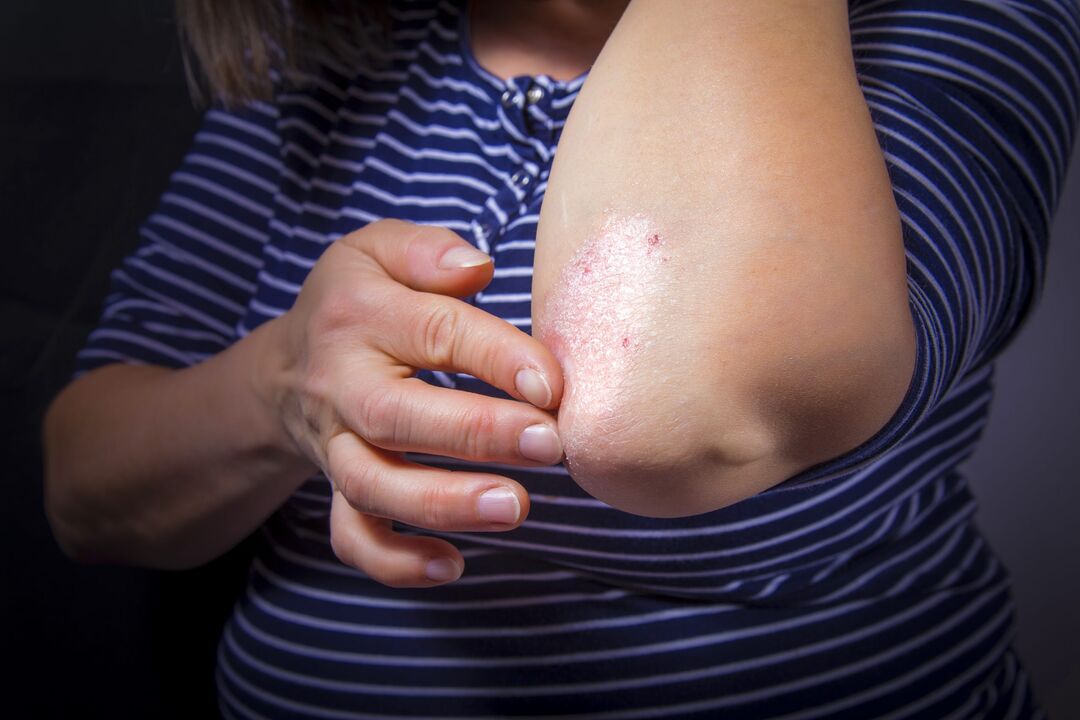
Psoriasis is a skin condition that causes red, scaly patches covered with silvery scales that itch. Psoriasis usually appears between the ages of 20 and 30 and is often hereditary.
This pathology is not an infectious disease. In addition to physical suffering, mild psoriasis can also cause serious psychological problems: low self-esteem, shame and social isolation. You cannot die from psoriasis, but the impact of this disease on a person's life is very serious.
Causes of psoriasis
The causes of psoriasis have not been fully identified. The mechanism of the disease involves a violation of the division of skin cells, which in turn causes a reaction of the immune system. Such a reaction is one of the autoimmune reactions, since it is a reaction to the failure of the body itself, and not to the intrusion of an external threat.
Is psoriasis contagious?
Psoriasis is not contagious, and being afraid to shake hands with a person with this disease is foolish and cruel.
As already mentioned, psoriasis is not an infectious disease, and many studies suggest that it is autoimmune in origin. In psoriasis, it is believed that immune T cells, which are supposed to attack foreign organisms, tragically mistakenly attack healthy skin cells. This leads to thickening of the upper layer, the epidermis, and an inflammatory process that penetrates deeper into the dermis.
The autoimmune theory of the origin of psoriasis has its place, but it has not yet been possible to find the autoantigen that should trigger this process, i. e. the i has not yet been crossed.
But it's clear: you can't catch psoriasis—you can only catch it.
Is psoriasis inherited?
Like rosacea, psoriasis is hereditary. The hereditary nature of psoriasis is confirmed by the fact that the frequency of occurrence is higher in families in which psoriasis has already been diagnosed, and the concentration of occurrence in twins is also higher than in other groups.
But heredity must be awakened. This happens as a result of provoking factors:
- psychological trauma and chronic stress conditions;
- previous infectious disease;
- skin injuries;
- some medications;
- hormonal changes in the body;
- allergy (for example, citrus fruits, eggs, chocolate can aggravate the disease);
- alcohol poisoning;
- even climate change.
Symptoms of psoriasis
The first symptoms of psoriasis: skin rashes in the form of bright pink plaques with a flaky surface. Plaques are single, rise above the level of healthy skin and are located on the elbows and popliteal cavities.
Psoriasis plaques most often appear on the skin of the knees, elbows, chest, abdomen, back and scalp, but as the disease progresses, they can also appear in any other, most unexpected place on the skin.
Initially, the papules are small - 3-5 mm, the color is bright pink. They gradually increase in size and are covered with silvery scales, and then merge into larger formations called plaques.
The fresh elements of the papules are usually brightly colored, even red, while the "old" ones are rather pale. In the initial stage of psoriasis, the edges of the papules do not peel off. They represent a hyperemic border - growth corolla
Psoriasis is characterized by the Auspitz triad. This triad can be observed when the surface of the papule is scraped with a sharp object. It includes three phenomena:
- the stearin spot phenomenon - the layering of a large number of silvery-white scales that can be easily separated when scraped;
- the symptom of psoriatic film is a detached surface consisting of a spinous layer, which opens after peeling off the lower layers of the corneum;
- the phenomenon of "blood dew" - the discovery of surface capillaries in the form of small blood spots after the detachment of the psoriasis film
Stages of psoriasis
Primary element of psoriasisa single pink or red papule covered with a large number of loose silvery-white scales.
Psoriasis develops quite slowly, and an increase in the number of plaques can be observed over several months or years. In a small percentage of patients, the disease may worsen. This is usually preceded by severe mental stress or a serious illness requiring massive medication. In this case, the papules are not pale pink, but bright red, with obvious signs of inflammation, swollen and itchy.
Second stagepsoriasis is characterized by more extensive lesions. New papules appear at the site of scratching, forming new plaques. As a result of growth, new growths merge with existing ones. Plaques affect symmetrical limbs and form similar patterns and lines.
In the third stagegrowth slows down, changes mainly affect the structure of the rash. The boundaries between healthy and affected skin become clearer. Plaques acquire a bluish tint and are actively shed. In the absence of therapy, they thicken and sometimes papillomatous nevus (brown) and warty growths (flesh-colored) develop.
There is another section -disease regression, in which case the symptoms disappear. Peeling stops, the definition of the border disappears, the skin normalizes and returns to its original state.
Types of psoriasis
- Spotted psoriasis is represented by pale pink, weakly infiltrated spots. It reminds me of toxicoderma.
- Irritable psoriasis - occurs due to exposure of the skin to aggressive environmental factors (sunlight, cold, heat) and irritating drugs. The color of the plaque becomes more intense, its size increases, it rises above the surface of the skin, and a reddish belt forms along the edges.
- Seborrheic psoriasis - often develops in seborrheic patients. The clinical picture is very similar to seborrheic eczema.
- Exudative psoriasis is quite common. It occurs due to the excessive secretion of inflammatory fluid - exudate. It impregnates the scales, turning them into a scale crust.
- Psoriasis of the palms and soles is represented either by ordinary plaques and papules or by hyperkeratotic formations similar to calluses and calluses.
- Follicular psoriasis is quite rare. The rash consists of white miliary nodules with a funnel-shaped depression in the center.
- Psoriasis of the mucosa is also rare. It occurs on the mucous membrane of the mouth and bladder. It appears as gray-white areas with a red border
Depending on the seasonality of the exacerbation, several types of psoriasis are distinguished:
- summer - exacerbation occurs as a result of exposure to sunlight on the skin;
- winter - occurs due to extreme cold affecting the skin.
In non-seasonal psoriasis, there are no periods of remission, the disease occurs all year round.
According to the affected skin area:
- limited psoriasis - occupies less than 20% of the skin of the body;
- common - more than 20%;
- generalized - the whole skin is affected.
In fact, the disease has several subtypes, and sometimes one patient develops two or three forms at the same time. Most often - in 80-90% of cases - plaque psoriasis develops.
30% of patients have psoriatic arthritis, in which the joints become inflamed with external manifestations, and 10% have the teardrop form of the disease.
Other, rarer subtypes are also known. All of them are manifested by rashes and itching in any part of the body, which is sometimes very painful. But there is good news: according to statistics, psoriasis appears in a mild form in 80% of cases, and the lesions cover less than 3% of the body surface.
Forms of psoriasis
- The pustular form of psoriasis. It is characterized by the presence of plaques with cortical scales impregnated with secretions. If there is an injury, such as scratching or self-harm in the folds of the body, the rash will be moist. They itch and burn and cause physical discomfort. This type of disease is more often diagnosed in people who are overweight, have hypothyroidism and diabetes.
- Pustular (generalized) form. It has a classic pattern of development, starting with a single vesicle that develops into plaques. Lesions are symmetrical and can affect any part of the body. The severe course of this form of psoriasis is characterized by the appearance of intraepidermal pustules. They can coalesce, forming "ponses of pus". The pustules do not open on their own, as they are protected by a thick brown crust on the outside.
- Arthropathic form. The most severe form of psoriasis, in which the changes first affect the small joints, then the large ones, including the spine. This is expressed by the symptoms of pain and their deformation. Probably joint fusion, loss of mobility. In the background of this form of psoriasis, other pathologies arise: ankylosis, osteoporosis, which leads to disability.
Complications
Many people know what psoriasis looks like, but the disease has many complications in addition to external manifestations. They are manifested in the deterioration of the skin's function, in the disturbance of temperature regulation and water-salt balance. The protective function against various bacteria also decreases.
For example, psoriasis on the hands is only part of the clinical picture. People with this diagnosis often suffer from chronic gastrointestinal and heart diseases.
Severe psoriasis is associated with an increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality in general.
The group of complications also includes:
- arthritis of psoriatic joints. About 30% of people with psoriasis will develop psoriatic arthritis during their lifetime, which is characterized by joint stiffness, pain and swelling. The disease can extend to joint damage. 80-90% of patients experience psoriatic nail lesions and onycholysis.
- psoriatic erythroderma;
- generalized pustular psoriasis;
- autoimmune diseases (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease);
- erectile dysfunction in men;
- metabolic syndrome, which is a combination of visceral obesity, insulin resistance and dyslipidemia.
It should also be noted that the pathologies associated with psoriasis, especially in severe forms, include depression, anxiety disorders, including suicidal tendencies.
Psoriatic erythroderma occurs somewhat less frequently. This condition occurs when the skin is completely damaged. Patients are concerned about itching and burning, excessive peeling of dead tissue, and a strong skin reaction to temperature changes.
The next most common type is pustular psoriasis. This complication is associated with the addition of a secondary infection - staphylococci and streptococci. Clinically, pustular psoriasis is associated with the appearance of pustules - pustules the size of buckwheat grains. Pustules appear in different places. They rise above the surface of the skin, are characterized by rapid growth and a tendency to merge. Existing symptoms are accompanied by high fever and signs of severe poisoning.
How is psoriasis diagnosed?
Psoriasis is diagnosed and treated by a dermatologist. Initially, an external examination of the affected areas is carried out and an anamnesis is collected. Sometimes the disease is similar to other diseases, especially in the first stage.
If the hands and nails are affected, it is important to exclude the presence of fungal infections. Seborrheic eczema, pityriasis rosea and papular syphilis must also be ruled out.
But I want to say that in most cases the diagnosis of psoriasis is not difficult, it does not even require an examination, it is enough to examine the skin.
Treatment of psoriasis
Can psoriasis be cured? Yes!
With the pathogenetic technique, the skin is brought to a state of perfect remission, the skin is cleansed, restored and the person can live a full life. Psoriasis is treated with the help of medicinal acids during the activation of points. The duration of the therapy is different for each patient and may require 6 or even 10 procedures. Maintenance therapy is required for 2-6 months, everything is individual.
I always warn patients that the treatment of psoriasis is torpid, that is, it progresses slowly. But we can take a long (about a month) break between procedures.
Home care is of great importance in the treatment of psoriasis. Homemade cosmetics consist of almost 99% natural ingredients. I spent about two years developing better formulas to protect skin with complex dermatoses at home.
The home care regimen for patients with psoriasis is selected individually. But there are also average regimens that are suitable for caring for skin suffering from psoriasis. Check out my social media. networks, there is an ocean of information.
Recommendations for eliminating the symptoms of the disease
I always tell my patients that effective treatment of any disease is possible only with an integrated approach. I would like to note that it is extremely important to take maximum precautions to reduce the risk of worsening the disease. As always, everything is banal and nothing new, but I'll say it anyway.
Recommended:
- avoid skin damage;
- avoid hypothermia;
- give up bad habits;
- avoid stressful situations;
- treat infections and concomitant illnesses immediately;
- Avoid prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
Psoriasis patients should be especially careful in observing personal hygiene requirements.
If you shower or bathe, then:
- use products without dyes and fragrances;
- choose a mild shampoo;
- avoid abrasive particles from rough sponges, creams, gels;
- Avoid harsh soap as it dries the skin too much;
- adjust the water temperature to keep it warm;
- do not stay in the water for more than 10-15 minutes;
- use a soft towel, do not rub or scratch the skin.
It is recommended to use special body moisturizers after showering and bathing. Try to comb as little as possible so as not to irritate the surface of the scalp. The same applies to hair drying. If you can't do without it, choose warm or cold streams.
Choose clothes that are lightweight, made from natural materials and loosely cut so they don't restrict movement or chafing.
Don't stay in the sun for too long in the summer. To protect your skin from UV rays, use high SPF sunscreens as part of a proper home care routine.
Psoriasis prevention
Based on the fact that psoriasis is considered a multifactorial disease, which partly includes immunopathological, genetic, endocrine, metabolic and possibly infectious components, there are no uniform rules for prevention.
Persons at risk must pay special attention to their health:
- whose relatives suffer from psoriasis;
- who frequently and continuously injure the skin;
- have chronic infections;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- endocrine disorders.
Increased nervousness, stress, alcohol abuse, frequent hypothermia and sunburn increase the likelihood of pathology.
If the treatment of psoriasis according to WHO standards (hormones, light therapy) did not help, come and let's remove this "snow paste" from your life. After all, without timely and competent treatment, psoriasis negatively affects vital organs and systems.